Navigating the complex labour laws governing employment practices is essential when running Rwanda payroll. However, building an in-house compliance team may not be the most efficient way to manage your remote team’s payroll in Rwanda.
Regardless of size, global companies need help to secure in-country expertise for localised payroll service. This is where a partner like Workforce Africa provides significant value in supporting global firms to maintain compliance when handling payroll in Rwanda, addressing every intricate detail, including;
- Salary computation requirements,
- Taxation legislation specifics (social security, employee income tax, corporate tax, VAT and other employee deductions.
- Benefits administration, and more (health insurance, pension, paid leaves, holiday compensation
Workforce Africa simplifies hiring and payroll compliance for offshore talent management in Rwanda. No need for a subsidiary or entity setup. From contracts and onboarding to taxes, payroll, and admin tasks, partnering with us – a payroll firm in Rwanda will help you focus on growth for greater levels of success.
Employment Contract Termination
In accordance with the laws of Rwanda, employment contracts can be terminated by either party upon giving notice depending on the terms of the contract. The employer may also terminate an employee’s contract without notice if there is just cause, such as gross misconduct or breach of contract. Conversely, an employee may terminate their contract by resigning in writing, which must be acknowledged by the employer. It is essential to follow the proper procedures for terminating an employment contract to avoid any potential legal disputes or penalties
Rwanda Country Overview
The Republic of Rwanda lies in East Africa. It is predominantly an English-speaking country. Two critical cities in Rwanda are Kigali, the capital and the economic hub, and Butare. These urban centres act as transit points to ecotourism destinations and beach resorts. With a population exceeding 14.2 million people, Rwanda boasts a significant demographic presence.
In recent years, key industries experiencing growth include textile, cement and agricultural products. Rwanda also boasts a market-based, diversified economy comprising petroleum imports, tourism, agriculture, and services. Considerations such as the low labour cost and abundant natural resources make Rwanda attractive for businesses seeking expansion opportunities.
Although Rwanda possesses a highly skilled workforce, hiring and establishing a team can be time-consuming and challenging. However, partnering with an Employer of Record (EOR) or Professional Employer Organisation (PEO) in Rwanda facilitates swift market entry. It manages all legal complexities associated with operations in the country.
Payroll Processing in Rwanda
Local labour laws in Rwanda govern payroll processing, with each employee’s salary potentially calculated differently. Due to compliance concerns, processing payroll at scale can become complex, cumbersome, and risky. Here are the phases of payroll processes global businesses should understand:
1. Pre-payroll Phase
Your organisation’s unique approach to payroll compliance shapes its policies and processes, including payroll preparation. Global firms must prioritise essential business elements in the pre-payroll phase, such as accurate business profile documentation and tailored work location policies, which is crucial. Customise leave and work policies to align with local standards in Rwanda to ensure compliance and transparency while collaborating closely with compliance teams or partners to help adhere to statutory requirements throughout the payroll management process for your remote team. In this phase also, standardising compensation packages to conform with local payment norms, such as payment cycles, which enhance compliance and meet employee expectations, is necessary.
2. Payroll Calculation Phase
Streamlining input collection and validation processes ensures accurate wage calculations in this phase of payroll processing. This phase involves the actual calculation of wages, with a primary focus on this task. Utilising software automation and digital document submission tools makes payroll calculations efficient and reduces the risk of human error in this process.
3. Post-payroll Phase
The post-payroll phase in Rwanda refers to the period after payroll processing, where employers review and settle any outstanding issues related to employee compensation, benefits, and taxes. This phase typically includes: salary payment, compliance reporting, benefit administration, audit and reconciliation. The post-payroll phase is crucial in Rwanda as it ensures that employers comply with regulatory requirements, maintain a good employer-employee relationship, and reduce the risk of penalties or fines associated with non-compliance.
Payroll Components in Rwanda
Here are some aspects comprehensively needed to navigate Rwanda’s payroll compliance:
- Salary/Wages
- Overtime benefits
- Social security contribution
- Paid leaves
- Paid holidays
- Payroll taxes
- Other laws
Navigating Rwanda Payroll Compliance
Rwanda’s employment regulation primarily revolves around Law No 66/2018 along with pertinent sections of other laws and acts. The Labor Law outlines critical aspects of payroll processing and compliance with crucial employment practices-:
- Salary/ Minimum Wage: There is no mandated minimum wage; instead, wage rates are determined by local industries.
- Working hours: Regular hours and overtime pay rates are set in the employment contracts or collective bargaining agreements. Stipulated work hours are typically 40 hours per week.
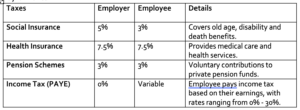
- Social Security Contribution: The Employer contributes 5%, while the Employee pays 3%.
- Health Insurance Scheme: Rwanda operates a compulsory healthcare system designed to ensure access to medical services for all citizens. The system, known as Mutuelle de Santé, is a community-based health insurance scheme that requires mandatory enrollment.
- Pension Contributions: Contributions to private pension schemes are voluntary and require the employee’s consent.
- Payroll Taxes:
Paid Leaves
- Annual Leave: Employees are entitled to 18 days of paid annual leave after completing one year of service. Furthermore, an additional day of paid leave is granted for every three consecutive years of service, up to a maximum of 21 days.
- Sick Leave: Sick leave is available for up to six months with proper documentation. The first three months are paid, while the remaining three months are unpaid.
- Maternity Leave: This amounts to a minimum of 14 weeks (over three months), including a mandatory two-week period to be taken prior to the due date.
- Paternity Leave: Employees are entitled to four working days of leave immediately following a delivery or miscarriage.
- Compassionate Leave: Employees are entitled to four days of compassionate leave, with the total leave not exceeding 10 working days in a calendar year.
- Paid Public Holidays: In Rwanda, the paid holidays are as follows:
- January 1: New Year’s Day
- January 2: Day after New Year’s Day
- February 2: National Heroes Day
- April: Good Friday (Date Varies)
- April 7: Genocide against the Tutsi Memorial Day
- May 1: Workers’ day
- June 1: Independence Day
- July 6: Liberation Day
- August 7: Umuganuara
- August 17: Assumption Day
- Eid Al Fatr: Based on the Islamic Calendar
- Eid Al Ahda: Based on the Islamic Calendar
- December 25: Christmas Day
- December 26: Boxing Day
Payroll Outsourcing in Rwanda
Payroll in Rwanda also encompasses termination and probationary periods law. Employees are not generally eligible for severance pay, except the termination is unjustified, or the employer voluntarily decides to make severance payment.
Collaborate with an Africa employer of record and payroll solutions provider such as Workforce Africa to strategically outsource your payroll operations while ensuring compliance with local labour regulations. Additionally, leverage our flexible service offerings to expand your international teams as needed.

